decision of the standing committee of the national peoples congress on amending the law of the peoples republic of china on the protection
Decision of the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress
on Amending the Law of the People's Republic of China on the
Protection of Rights and Interests of Women
Order of the President of the People’s Republic of China No.40
The Decision of the Standing Committee of the National People’s
Congress on Amending the Law of the People’s Republic of China on the
Protection of Rights and Interests of Women, adopted at the 17th
Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Tenth National People’s
Congress of the People’s Republic of China on August 28, 2005, is
hereby promulgated and shall go into effect as of December 1, 2005.
Hu Jintao
President of the People’s Republic of China
August 28, 2005
Decision of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress
on Amending the Law of the People’s Republic of China on the
Protection of Rights and Interests of Women
(Adopted at the 17th Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Tenth
National People’s Congress on August 28, 2005)
At its 17th Meeting, the Standing Committee of the Tenth National
People’s Congress decided to make the following amendments to the Law
of the People’s Republic of China on the Protection of Rights and
Interests of Women:
1. Article 2 is revised to read: "Women shall enjoy equal rights with
men in all aspects of political, economic, cultural, social and family
life.
"Equality between men and women is a basic State policy. The State
takes the necessary measures to gradually improve the systems for
protecting the rights and interests of women, in order to eliminate
all forms of discrimination against women.
"The State protects the special rights and interests enjoyed by women
according to law.
"Discriminating against, maltreating, abandoning, and physically
abusing women are prohibited."
2. One article is added as Article 3, which reads: " The State Council
shall formulate an outline for the development of Chinese women and
include such outline in the national economic and social development
plan.
"Local people’s governments at or above the county level shall, in
accordance with the outline for the development of Chinese women,
formulate programs for the development of women in their respective
administrative regions and include the programs in their national
economic and social development plans."
3. Article 4 is changed to be Article 6 and is revised to read: "
People’s government at all levels shall attach great importance to and
strengthen the protection of the rights and interests of women.
"Institutions in charge of work for women and children under the
people’s governments at or above the county level shall be responsible
to organize, coordinate, direct and urge the relevant departments
concerned to ensure the protection of women’s rights and interests.
"The relevant departments of the people’s governments at or above the
county level shall, within the scope of their duties, ensure the
protection of women’s rights and interests."
4. Article 5 is changed to be Article 7 and is revised to read: "The
All-China Women’s Federation and local women’s federations at various
levels shall, in accordance with law and the Constitution of the
All-China Women’s Federation, represent and uphold the interests of
women of all nationalities and all walks of life, and strive to
safeguard the rights and interests of women.
"The trade unions and the Communist Youth League organizations shall,
within the scope of their respective work, strive to safeguard the
rights and interests of women."
5. Article 9 is changed to be Article 10, and two paragraphs are added
as the second and third paragraph, which read: " When formulating
laws, regulations, rules and public policies, the relevant departments
shall, where major questions related to women’s rights and interests
are concerned, listen to the opinions of the women’s federations.
"Women and women’s organizations shall have the right to advance their
opinions and suggestions to State organs at various levels with regard
to protection of the rights and interests of women."
6.Article 10 is changed to be Article 11, and the second paragraph is
revised to read: "Among deputies to the National People’s Congress and
local people’s congresses at various levels, there shall be an
appropriate number of women deputies. The State takes measures to
gradually increase the proportion of the women deputies among deputies
to the National People’s Congress and local people’s congresses at
various levels."
One paragraph is added as the third paragraph, which reads: " Among
members of the residents’ committees and villager’s committees, there
shall be an appropriate number of women members."
7. Article 11 is changed to be Article 12, and the second paragraph is
revised to read: "State organs, public organizations, enterprises and
institutions shall, in training, selecting and appointing cadres,
adhere to the principle of equality between men and women, and there
shall be an appropriate number of women leading members."
8. Article 12 is changed to be Article 13, and one paragraph is added
as the first paragraph, which reads: "The All-China Women’s Federation
and local women’s federations at various levels shall represent women
to take an active part in democratic decision-making, management and
supervision of State and social affairs."
9. Article 15 is changed to be Article 16, and one paragraph is added
as the second paragraph, which reads: "With exception of special
subjects, no schools shall, in enrolling students, refuse to enroll
women on the pretext of sex or raise the enrollment standards for
women."
10. Article 17 is changed to be Article 18, and the third paragraph is
revised to read: " The governments, society and schools shall take
effective measures to solve the actual difficulties of female
school-age children or adolescents in schooling and create the
necessary conditions to ensure that the needy, disabled and migrant
female school-age children or adolescents finish compulsory
education."
11. Article 19 is changed to be Article 20 and is revised to read:
"People’s governments at various levels and the departments concerned
shall, in light of the need of urban and rural women, take measures to
organize women in receiving vocational education and practical
technological training."
12. The heading of Chapter IV is revised to read: " Rights and
Interests Relating to Work and Social Security. "
13. Article 21 is changed to be Article 22 and is revised to read: "
The State guarantees that women enjoy equal rights, with men, to work
and to social security."
14. Article 22 is changed to be Article 23, and one paragraph is added
as the second paragraph, which reads: "When employing female workers
and staff members, the employing units shall, according to law,
conclude labour (or employment) contracts or service agreements with
them. No clauses that restrict marriage and childbearing of female
workers and staff members shall be proscribed in the labour (or
employment) contracts or the service agreements."
The second paragraph is changed to be the third paragraph, which
reads: "Employing of female minors under the age of 16, except where
otherwise prescribed by the State, is prohibited."
15. Article 23 is changed to be Article 24 and is revised to read:
"Equal pay for equal work shall be applied to men and women alike.
Women shall enjoy equal rights with men in receiving welfare
benefits."
16. Article 26 is changed to be Article 27 and is revised to read: "
No unit shall reduce the salaries or wages of female workers and staff
members, or dismiss them, or unilaterally cancel the labour (or
employment) contracts or service agreements with them because they are
married, pregnant, on maternity leave or breast-feeding, except where
female workers and staff members request termination of the labour (or
employment) contracts or service agreements themselves.
"In implementing the retirement system of the State, no unit shall
discriminate against women on the pretext of sex."
17.Article 27 is changed to be Article 28 and is revised to read: "
The State develops social insurance, social relief, social welfare and
medical and health services to guarantee that women enjoy social
insurance, social relief, social welfare and health care services, and
other rights and interests.
" The State advocates and encourages public welfare activities that
aim to help women."
18. One article is added as Article 29, which reads: " The State
promotes a childbearing insurance system, and establishes other sound
security systems relating to childbearing.
"Local people’s governments at various levels and the departments
concerned shall, in accordance with relevant regulations, provide the
necessary childbearing relief to needy women."
19. Article 30 is changed to be Article 32 and is revised to read:
"Women shall enjoy equal rights with men in contracted management of
land, distribution of the earnings of the collective economic
organizations, use of the compensations for expropriated or
requisitioned land and use of housing sites in rural areas."
20.One article is added as Article 33, which reads: "No organizations
or individuals shall infringe upon women’s rights and interests in
rural collective economic organizations on the pretext of their being
single, married, divorced and widowed.
"If a man moves to the domicile of a woman for marriage, the man and
his children shall enjoy equal rights and interests with the other
members of the rural collective economic organizations at the place of
their residence."
21. Article 35 is changed to be Article 38 and is revised to read:
"Women’s right of life and health is inviolable. Drowning, abandoning
or cruel infanticide in any manner of female babies is prohibited;
discriminating against or maltreating of women who give birth to
female babies or women who are sterile is prohibited; cruel treatment
causing bodily injury to or death of women by means of superstition or
violence is prohibited; maltreating or abandoning of women who are
ill, disabled or aged is prohibited."
22. Article 36 is changed to be Article 39 and is revised to read:
"Abducting of, trafficking in, or kidnapping of women is prohibited;
buying of women who are abducted, trafficked in, or kidnapped is
prohibited; obstructing the rescue of women who are abducted,
trafficked in, or kidnapped is prohibited.
"People’s governments at various levels and the departments of public
security, civil affairs, labour and social security, and health shall,
in compliance with their respective duties, take timely measures to
rescue women who are abducted, trafficked in or kidnapped and well
settle the problems arising thereafter, and women’s federations shall
assist and cooperate with the governments and departments in doing a
good job of the above. No one shall discriminate against the women who
are abducted, trafficked in, or kidnapped."
23. One article is added as Article 40, which reads: "Sexual
harassment against women is prohibited. The female victims shall have
the right to file complaints with the units where they work and the
departments concerned."
24. Article 37 is changed to be Article 41, and the second paragraph
is revised to read: "Arranging for, forcing or luring women to engage
in prostitution, providing shelters for prostitution, or instigating
women to engage in prostitution, or acting indecently against women is
prohibited."
One paragraph is added as the third paragraph, which reads: "Arranging
for, forcing or luring women to give obscene performances is
prohibited."
25. Articles 38 and 39 are merged into one article as Article 42 and
are revised to read: "Women’s rights of personality, including their
right of reputation, right of honor, right of privacy and right of
portrait, shall be protected by law.
" Besmirching women’s personal dignity by such means as humiliation
and libel is prohibited. Decrying or besmirching women’s personality
through the mass media or by other means is prohibited. The use of a
woman’s portrait for profit-making purposes in advertisements,
trademarks, window display, newspapers, magazines, books, audio-video
products, electronic publications, internet, etc., without the women’s
personal consent, is prohibited."
26. Article 42 is changed to be Article 45 and is revised to read: "A
husband shall not apply for a divorce when his wife is pregnant, or is
within one year after the birth of the child, or within six months
after the termination of her gestation. This restriction shall not
apply in a case where the wife applies for a divorce, or where the
people's court deems it necessary to accept the application for
divorce made by the husband."
27. One article is added as Article 46, which reads: "Domestic
violence against women is prohibited.
"The State takes measures to prevent and stop domestic violence.
"The departments of public security, civil affairs, judicial
administration, etc., as well as urban and rural mass organizations of
self-governance at the grass-roots level and public organizations
shall, within the scope of their respective duties, prevent and stop
domestic violence, and provide succour to female victims."
28. Article 43 is changed to be Article 47, and one paragraph is added
as the second paragraph, which reads: "Where the husband and the wife
agree in writing that the property acquired separately by them during
the period in which their wedlock exists is owned by them likewise,
and the wife has been shouldering more duties in respect of bringing
up the child, taking care of the old, assisting the husband in work,
etc., she shall, at the time of divorce, have the right to request the
husband to make compensation for the above."
29. Article 44 is changed to be Article 48, the first and fourth
paragraphs are deleted, and this Article is revised to read: "At the
time of divorce, the husband and the wife shall seek agreement
regarding the disposition of their jointly possessed houses; if they
fail to reach an agreement, the people's court shall make a judgment
in light of the actual conditions of both parties and in adhering to
the principle of taking into consideration the rights and interests of
their child (children) and the wife, except where otherwise agreed
upon by the two parties.
"In a case where the husband and the wife jointly rent a house or a
room, the wife's housing problem shall, at the time of divorce, be
solved according to the principle of taking into consideration the
rights and interests of their child (children) and the wife."
30. Article 47 is changed to be Article 51, and one paragraph is added
as the third paragraph, which reads: "The State institutes a system of
premarital health care and health care for the pregnant and lying-in
periods and develops the maternal and infant health care undertakings.
People’s governments at various levels shall take measures to ensure
women’s access to technical services for family planning in order to
improve their reproductive health."
31. The first paragraph of Article 48 is changed to be Article 52 and
is revised to read: "When a woman's lawful rights and interests are
infringed upon, she has the right to request the department concerned
for disposition according to law, or according to law, apply to an
arbitral body for arbitration, or bring a lawsuit in a people's court.
"Where a woman in strained circumstances needs legal aid or judicial
relief, the local legal aid institution or people’s court shall help
her and provide her with legal aid or judicial relief in accordance
with law."
32. The second paragraph of Article 48 is changed to be Article 53 and
is revised to read: "When a woman's lawful rights and interests are
infringed upon, she may file a complaint with a women's organization,
which shall protect the lawful rights and interests of the victim and
have the right to request and help the department or unit concerned to
investigate and deal with the case. The said department or unit shall
investigate and deal with the case according to law and give a reply
afterwards." 33.One article is added as Article 54, which reads:
"Women’s organizations shall support the women victims who need help
in lawsuits. " A women’s federation or a women’s organization
concerned may expose and criticize through the mass media the acts
infringing upon the lawful rights and interests of special groups of
women, and shall have the right to request the department concerned to
investigate and deal with the cases according to law."
34. Subparagraph (5) under the first paragraph of Article 50 is
changed to be Article 55 and is revised to read: "Where an entity, in
violation of the provisions of this Law, infringes upon a woman’s
rights and interests in a rural collective economic organization on
the pretext of her being single, married, divorced or widowed, or
infringes upon the equal rights and interests enjoyed by a man, who
moves to the domicile of a woman for marriage, and his children with
the members of the rural collective economic organization at the place
of their residence, the township people’s government shall mediate in
accordance with law; the victims on their part may, according to law,
apply for arbitration to an arbitral body specialized in matters of
rural land contracts, or bring a suit in a people’s court, which shall
accept the case according to law."
35. Articles 49 and 52 are merged into one article as Article 56,
which is revised to read: "Where administrative sanctions are
prescribed by other laws and regulations for the infringement upon the
lawful rights and interests of women in violation of the provisions of
this Law, the provisions of those laws and regulations shall prevail;
where such an infringement causes loss of property or other damages,
the infringer shall bear civil responsibilities according to law; if a
crime is constituted, criminal responsibilities shall be investigated
according to law."
36. Article 50 is changed to be Article 57 and is revised to read:
"Where a person, in violation of the provisions of this Law, evades,
delays or suppresses the investigation and disposition of a complaint,
a charge or an exposure regarding the infringement upon a woman’s
rights and interests, or retaliates against the woman who make the
compliant, charge or exposure, the unit where the person works or the
department in charge or at a higher level shall instruct him to
rectify, and give administrative sanctions according to law to the
person directly in charge of the unit and the other persons directly
responsible. "Where a State organ and its functionaries fail to
perform their duties according to law, or fail to stop, in a timely
manner, the acts infringing upon the lawful rights and interests of
women or to provide the women victims with the necessary help, thus
serious consequences ensue, the unit where the organ and its
functionaries belong or the organ at a higher level shall, according
to law, give administrative sanctions to the person directly in charge
of the State organ and the other persons directly responsible. "Where
a person, in violation of the provisions of this Law, infringes upon
women’s rights and interests relating to culture and education, to
work and social security, to the person and property, and to marriage
and family, the unit where the person belongs or the department in
charge or at a higher level shall instruct him to rectify; and the
person directly in charge and the other persons directly responsible,
if they are State functionaries, shall be given administrative
sanctions according to law by the units where they belong or by an
organ at a higher level."
37. One article is added as Article 58, which reads: " Where a person,
in violation of the provisions of this Law, commits sexual harassment
or domestic violence against a woman, if such act constitutes a
violation of the regulations for administration of public security,
the victim may apply to a public security organ for an administrative
sanction against the violator according to law, and may also bring a
civil suit in a people’s court according to law."
38. Article 51 is changed to be Article 59 and is revised to read:
"Where an entity, in violation of the provisions of this Law, decries
and damages a woman’s personality through the mass media or by other
means, the department of culture, radio, film and television, the
press and publication, or a relevant department shall, in compliance
with their respective functions and powers, instruct it to rectify and
give it an administrative sanction according to law."
39. Article 53 is changed to be Article 60 and the first paragraph is
deleted; the second paragraph is changed to be the first paragraph;
the third paragraph is changed to be the second paragraph; and they
are revised to read: "The standing committees of the people's
congresses of provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities
directly under the Central Government may formulate measures for
implementation on the basis of this Law.
"The people's congresses of national autonomous areas may formulate
regulations with appropriate adaptations or supplements in accordance
with the principles laid down in this Law and in light of the specific
conditions of the local ethnic women. The regulations formulated by
autonomous regions shall be submitted to the Standing Committee of the
National People's Congress for approval before going into effect; the
regulations formulated by autonomous prefectures or autonomous
counties shall be submitted to the standing committees of the people's
congresses of the relevant provinces, autonomous regions, or the
municipalities directly under the Central Government for approval
before going into effect, and shall be submitted to the Standing
Committee of the National People's Congress for the record."
This Decision shall go into effect as of December 1, 2005.
The Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Protection of Rights
and Interests of Women shall be promulgated anew after the revisions
are made according to this Decision and the order of the articles is
rearranged accordingly.
Law of the People's Republic of China on the Protection of Rights and
Interests of Women
(Adopted at the Fifth Session of the Seventh National People's
Congress on April 3, 1992, and amended in accordance with the Decision
on Amending the Law of the People’s Republic of China on the
Protection of Rights and Interests of Women adopted at the 17th
Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Tenth National People’s
Congress on August 28, 2005)
Contents
Chapter I General Provisions
Chapter II Political Rights
Chapter III Rights and Interests Relating to Culture and Education
Chapter IV Rights and Interests Relating to Work and Social
Security
Chapter V Rights and Interests Relating to Property
Chapter VI Rights Relating to the Person
Chapter VII Rights and Interests Relating to Marriage and Family
Chapter VIII Legal Responsibility
Chapter IX Supplementary Provisions
Chapter I General Provisions
Article 1 In accordance with the Constitution and the actual
conditions of the country, this Law is formulated to protect women's
lawful rights and interests, promote the equality between men and
women and allow full play to women's role in socialist modernization.
Article 2 Women shall enjoy equal rights with men in all aspects of
political, economic, cultural, social and family life.
Equality between men and women is a basic State policy. The State
takes the necessary measures to gradually improve the systems for
protecting the rights and interests of women, in order to eliminate
all forms of discrimination against women.
The State protects the special rights and interests enjoyed by women
according to law.
Discriminating against, maltreating, abandoning, and physically
abusing women are prohibited.
Article 3 The State Council shall formulate an outline for the
development of Chinese women and include such outline in the national
economic and social development plan.
Local people’s governments at or above the county level shall, in
accordance with the outline for the development of Chinese women,
formulate programs for the development of women in their respective
administrative regions and include the programs in their national
economic and social development plans.
Article 4 The protection of women's lawful rights and interests is a
common responsibility of the whole society. State organs, public
organizations, enterprises and institutions as well as urban and rural
mass organizations of self-government at the grass-roots level shall,
in accordance with the provisions of this Law and other relevant laws,
protect women's rights and interests.
The State takes effective measures to provide necessary conditions for
women to exercise their rights according to law.
Article 5 The State encourages women to cultivate a sense of
self-respect, self-confidence, self-reliance and self-strengthening,
and to safeguard their own lawful rights and interests by utilizing
law.
Women shall abide by the laws of the State, respect social morality
and perform their obligations prescribed by law.
Article 6 People’s government at all levels shall attach great
importance to and strengthen the protection of the rights and
interests of women.
Institutions in charge of work for women and children under the
people’s governments at or above the county level shall be responsible
to organize, coordinate, direct and urge the relevant departments
concerned to ensure the protection of women’s rights and interests.
The relevant departments of the people’s governments at or above the
county level shall, within the scope of their duties, ensure the
protection of women’s rights and interests.
Article 7 The All-China Women’s Federation and local women’s
federations at various levels shall, in accordance with law and the
Constitution of the All-China Women’s Federation, represent and uphold
the interests of women of all nationalities and all walks of life, and
strive to safeguard the rights and interests of women.
The trade unions and the Communist Youth League organizations shall,
within the scope of their respective work, strive to safeguard the
rights and interests of women.
Article 8 People's governments at various levels and relevant
departments shall commend and award those organizations and
individuals that have made notable achievements in the protection of
women's lawful rights and interests.
Chapter II Political Rights
Article 9 The State guarantees that women enjoy equal political rights
with men.
Article 10 Women have the right to conduct State affairs, manage
economic and cultural undertakings and administer social affairs
through various channels and in various ways.
When formulating laws, regulations, rules and public policies, the
relevant departments shall, where major questions related to women’s
rights and interests are concerned, listen to the opinions of the
women’s federations.
Women and women’s organizations shall have the right to advance their
opinions and suggestions to State organs at various levels with regard
to protection of the rights and interests of women.
Article 11 Women enjoy the equal right, with men, to vote and to stand
for election.
Among deputies to the National People’s Congress and local people’s
congresses at various levels, there shall be an appropriate number of
women deputies. The State takes measures to gradually increase the
proportion of the women deputies among deputies to the National
People’s Congress and local people’s congresses at various levels.
Among members of the residents’ committees and villager’s committees,
there shall be an appropriate number of women members.
Article 12 The State actively trains and selects female cadres.
State organs, public organizations, enterprises and institutions
shall, in training, selecting and appointing cadres, adhere to the
principle of equality between men and women, and there shall be an
appropriate number of women leading members.
The State attaches great importance to the training and selection of
female cadres of minority nationalities.
Article 13 The All-China Women’s Federation and local women’s
federations at various levels shall represent women to take an active
part in democratic decision-making, management and supervision of
State and social affairs.
Women's federations at various levels and their member organizations
may recommend female cadres to State organs, public organizations,
enterprises or institutions.
Article 14 The departments concerned shall listen to and accept
criticisms or rational suggestions regarding the protection of women's
rights and interests; with respect to complaints or charges against,
or exposures of infringement upon women's rights and interests, the
departments concerned must ascertain the facts, and be responsible for
their disposition; no organization or individual may suppress such
complaints, charges or exposures or resort to retaliation.
Chapter III Rights and Interests Relating to Culture and Education
Article 15 The State guarantees that women enjoy equal rights with men
with respect to culture and education.
Article 16 Schools and departments concerned shall, by implementing
the relevant regulations of the State, guarantee that women enjoy
equal rights with men in such aspects as starting school, entering a
higher school, job assignment upon graduation, conferment of academic
degrees and dispatch for study abroad.
With exception of special subjects, no schools shall, in enrolling
students, refuse to enroll women on the pretext of sex or raise the
enrollment standards for women.
Article 17 Schools shall, in line with the characteristics of female
adolescents, take measures in respect of education, management and
facilities so as to ensure female adolescents' sound development in
body and in mind.
Article 18 Parents or other guardians must perform their duty of
ensuring that female school-age children or adolescents receive the
compulsory education.
Where parents or other guardians fail to send female school-age
children or adolescents to school, the local people's governments
shall admonish and criticize them and, by adopting effective measures,
order them to send their female school-age children or adolescents to
school, with the exception of those who, on account of illness or
other special circumstances, are allowed by the local people's
governments not to go to school.
The governments, society and schools shall take effective measures to
solve the actual difficulties of female school-age children or
adolescents in schooling and create the necessary conditions to ensure
that the needy, disabled and migrant female school-age children or
adolescents finish compulsory education.
Article 19 People's governments at various levels shall, in accordance
with relevant regulations, incorporate the work of elimination of
illiteracy or semi-literacy among women into plans for illiteracy
elimination and post-elimination education, adopt organizational forms
and working methods suitable to women's characteristics, and organize
and supervise the relevant departments in the implementation of such
plans.
Article 20 People’s governments at various levels and the departments
concerned shall, in light of the need of urban and rural women, take
measures to organize women in receiving vocational education and
practical technological training.
Article 21 State organs, public organizations, enterprises and
institutions shall, by implementing relevant regulations of the State,
ensure that women enjoy equal rights with men in their participation
in scientific, technological, literary, artistic and other cultural
activities.
Chapter IV Rights and Interests Relating to Work and Social Security
Article 22 The State guarantees that women enjoy equal rights, with
men, to work and to social security.
Article 23 With exception of the special types of work or post
unsuitable to women, no unit may, in employing staff and workers,
refuse to employ women by reason of sex or raise the employment
standards for women.
When employing female workers and staff members, the employing units
shall, according to law, conclude labour (or employment) contracts or
service agreements with them. No clauses that restrict marriage and
childbearing of female workers and staff members shall be proscribed
in the labour (or employment) contracts or the service agreements.
Employing of female minors under the age of 16, except where otherwise
prescribed by the State, is prohibited.
Article 24 Equal pay for equal work shall be applied to men and women
alike. Women shall enjoy equal rights with men in receiving welfare
benefits.
Article 25 In such aspects as promotion in post or in rank, evaluation
and determination of professional and technological titles, the
principle of equality between men and women shall be upheld and
discrimination against women shall not be allowed.
Article 26 All units shall, in line with women's characteristics and
according to law, protect women's safety and health during their work
or physical labour, and shall not assign them any work or physical
labour not suitable to women.
Women shall be under special protection during menstrual period,
pregnancy, obstetrical period and nursing period.
Article 27 No unit shall reduce the salaries or wages of female
workers and staff members, or dismiss them, or unilaterally cancel the
labour (or employment) contracts or service agreements with them
because they are married, pregnant, on maternity leave or
breast-feeding, except where female workers and staff members request
termination of the labour (or employment) contracts or service
agreements themselves.
In implementing the retirement system of the State, no unit shall
discriminate against women on the pretext of sex.
Article 28 The State develops social insurance, social relief, social
welfare and medical and health services to guarantee that women enjoy
social insurance, social relief, social welfare and health care
services, and other rights and interests.
The State advocates and encourages public welfare activities that aim
to help women.
Article 29 The State promotes a childbearing insurance system, and
establishes other sound security systems relating to childbearing.
Local people’s governments at various levels and the departments
concerned shall, in accordance with relevant regulations, provide the
necessary childbearing relief to needy women.
Chapter V Rights and Interests Relating to Property
Article 30 The State guarantees that women enjoy the equal right, with
men, to property.
Article 31 In joint property relationship derived from marriage or
family, the rights and interests enjoyed by women according to law may
not be infringed upon.
Article 32 Women shall enjoy equal rights with men in contracted
management of land, distribution of the earnings of the collective
economic organizations, use of the compensations for expropriated or
requisitioned land and use of housing sites in rural areas.
Article 33 No organizations or individuals shall infringe upon women’s
rights and interests in rural collective economic organizations on the
pretext of their being single, married, divorced and widowed.
If a man moves to the domicile of a woman for marriage, the man and
his children shall enjoy equal rights and interests with the other
members of the rural collective economic organizations at the place of
their residence.
Article 34 Women's equal right, with men, of succession to property is
protected by law. Among the statutory successors in the same order,
women shall not be discriminated against. Widowed women have the right
to dispose of the property inherited by them, and no one may interfere
with the disposition thereof.
Article 35 Widowed women who have made predominant contributions in
maintaining their parents-in-law shall be regarded as the statutory
successors first in order, and their rights of succession thereto
shall not be affected by inheritance in subrogation.
Chapter VI Rights Relating to the Person
Article 36 The State guarantees that women enjoy equal rights with men
relating to their persons.
Article 37 Women's freedom of the person is inviolable. Unlawful
detention or deprivation or restriction of women's freedom of the
person by other illegal means is prohibited; and unlawful body search
of women is prohibited.
Article 38 Women’s right of life and health is inviolable. Drowning,
abandoning or cruel infanticide in any manner of female babies is
prohibited; discriminating against or maltreating of women who give
birth to female babies or women who are sterile is prohibited; cruel
treatment causing bodily injury to or death of women by means of
superstition or violence is prohibited; maltreating or abandoning of
women who are ill, disabled or aged is prohibited.
Article 39 Abducting of, trafficking in, or kidnapping of women is
prohibited; buying of women who are abducted, trafficked in, or
kidnapped is prohibited; obstructing the rescue of women who are
abducted, trafficked in, or kidnapped is prohibited.
People’s governments at various levels and the departments of public
security, civil affairs, labour and social security, and health shall,
in compliance with their respective duties, take timely measures to
rescue women who are abducted, trafficked in or kidnapped and well
settle the problems arising thereafter, and women’s federations shall
assist and cooperate with the governments and departments in doing a
good job of the above. No one shall discriminate against the women who
are abducted, trafficked in, or kidnapped.
Article 40 Sexual harassment against women is prohibited. The female
victims shall have the right to file complaints with the units where
they work and the departments concerned.
Article 41 Prostitution or whoring shall be prohibited.
Arranging for, forcing or luring women to engage in prostitution,
providing shelters for prostitution, or instigating women to engage in
prostitution, or acting indecently against women is prohibited.
Arranging for, forcing or luring women to give obscene performances is
prohibited.
Article 42 Women’s rights of personality, including their right of
reputation, right of honor, right of privacy and right of portrait,
shall be protected by law.
Besmirching women’s personal dignity by such means as humiliation and
libel is prohibited. Decrying or besmirching women’s personality
through the mass media or by other means is prohibited. The use of a
woman’s portrait for profit-making purposes in advertisements,
trademarks, window display, newspapers, magazines, books, audio-video
products, electronic publications, internet, etc., without the women’s
personal consent, is prohibited.
Chapter VII Rights and Interests Relating to Marriage and Family
Article 43 The State guarantees that women enjoy equal rights with men
in marriage and family.
Article 44 The State protects women's right of self-determination in
marriage. Interference with women's freedom of marriage or divorce
shall be prohibited.
Article 45 A husband shall not apply for a divorce when his wife is
pregnant, or is within one year after the birth of the child, or
within six months after the termination of her gestation. This
restriction shall not apply in a case where the wife applies for a
divorce, or where the people's court deems it necessary to accept the
application for divorce made by the husband.
Article 46 Domestic violence against women is prohibited.
The State takes measures to prevent and stop domestic violence.
The departments of public security, civil affairs, judicial
administration, etc., as well as urban and rural mass organizations of
self-government at the grass-roots level and public organizations
shall, within the scope of their respective duties, prevent and stop
domestic violence, and provide succour to female victims.
Article 47 A woman shall enjoy equal rights with her spouse in
possessing, utilizing, profiting from and disposing of the property
jointly possessed by the husband and wife according to law, which
shall not be affected by the status of income of either party.
Where the husband and the wife agree in writing that the property
acquired separately by them during the period in which their wedlock
exists is owned by them likewise, and the wife has been shouldering
more duties in respect of bringing up the child, taking care of the
old, assisting the husband in work, etc., she shall, at the time of
divorce, have the right to request the husband to make compensation
for the above.
Article 48 At the time of divorce, the husband and the wife shall seek
agreement regarding the disposition of their jointly possessed houses;
if they fail to reach an agreement, the people's court shall make a
judgment in light of the actual conditions of both parties and in
adhering to the principle of taking into consideration the rights and
interests of their child (children) and the wife, except where
otherwise agreed upon by the two parties.
In a case where the husband and the wife jointly rent a house or a
room, the wife's housing problem shall, at the time of divorce, be
solved according to the principle of taking into consideration the
rights and interests of their child (children) and the wife.
Article 49 Both parents enjoy the equal right to guardianship of their
minor child (children).
In a case where the father is deceased, incapacitated or under any
other circumstances that make him unable to act as the guardian of a
minor child (children), nobody may interfere with the mother's right
of guardianship.
Article 50 At the time of divorce, if the wife becomes sterile because
of the sterilization operation or any other reasons, the problem to
bring up the child (children) shall be so handled that, while to the
advantage of the rights and interests of the child (children), due
consideration shall be given to the wife's reasonable demands.
Article 51 Women have the right to child-bearing in accordance with
relevant regulations of the State as well as the freedom not to bear
any child.
Where a couple of child-bearing age practise family planning according
to the relevant regulations of the State, the departments concerned
shall provide safe and effective contraceptives and techniques, and
ensure the health and safety of the woman receiving any birth-control
operation.
The State institutes a system of premarital health care and health
care for the pregnant and lying-in periods and develops the maternal
and infant health care undertakings. People’s governments at various
levels shall take measures to ensure women’s access to technical
services for family planning in order to improve their reproductive
health.
Chapter VIII Legal Responsibility
Article 52 When a woman's lawful rights and interests are infringed
upon, she has the right to request the department concerned for
disposition according to law, or according to law, apply to an
arbitral body for arbitration, or bring a lawsuit in a people's court.
Where a woman in strained circumstances needs legal aid or judicial
relief, the local legal aid institution or people’s court shall help
her and provide her with legal aid or judicial relief in accordance
with law. When a woman's lawful rights and interests are infringed
upon, she may file a complaint with a women's organization, which
shall request the department or unit concerned to investigate and deal
with the case so as to protect the lawful rights and interests of the
complainant.
Article 53 When a woman's lawful rights and interests are infringed
upon, she may file a complaint with a women's organization, which
shall protect the lawful rights and interests of the victim and have
the right to request and help the department or unit concerned to
investigate and deal with the case. The said department or unit shall
investigate and deal with the case according to law and give a reply
afterwards.
Article 54 Women’s organizations shall support the women victims who
need help in lawsuits. A women’s federation or a women’s organization
concerned may expose and criticize through the mass media the acts
infringing upon the lawful rights and interests of special groups of
women, and shall have the right to request the department concerned to
investigate and deal with the cases according to law.
Article 55 Where an entity, in violation of the provisions of this
Law, infringes upon a woman’s rights and interests in a rural
collective economic organization on the pretext of her being single,
married, divorced or widowed, or infringes upon the equal rights and
interests enjoyed by a man, who moves to the domicile of a woman for
marriage, and his children with the members of the rural collective
economic organization at the place of their residence, the township
people’s government shall mediate in accordance with law; the victims
on their part may, according to law, apply for arbitration to an
arbitral body specialized in matters of rural land contracts, or bring
a suit in a people’s court, which shall accept the case according to
law.
Article 56 Where administrative sanctions are prescribed by other laws
and regulations for the infringement upon the lawful rights and
interests of women in violation of the provisions of this Law, the
provisions of those laws and regulations shall prevail; where such an
infringement causes loss of property or other damages, the infringer
shall bear civil responsibilities according to law; if a crime is
constituted, criminal responsibilities shall be investigated according
to law.
Article 57 Where a person, in violation of the provisions of this Law,
evades, delays or suppresses the investigation and disposition of a
complaint, a charge or an exposure regarding the infringement upon a
woman’s rights and interests, or retaliates against the woman who make
the compliant, charge or exposure, the unit where the person works or
the department in charge or at a higher level shall instruct him to
rectify, and give administrative sanctions according to law to the
person directly in charge of the unit and the other persons directly
responsible. Where a State organ and its functionaries fail to perform
their duties according to law, or fail to stop, in a timely manner,
the acts infringing upon the lawful rights and interests of women or
to provide the women victims with the necessary help, thus serious
consequences ensue, the unit where the organ and its functionaries
belong or the organ at a higher level shall, according to law, give
administrative sanctions to the person directly in charge of the State
organ and the other persons directly responsible.
Where a person, in violation of the provisions of this Law, infringes
upon women’s rights and interests relating to culture and education,
to work and social security, to the person and property, and to
marriage and family, the unit where the person belongs or the
department in charge or at a higher level shall instruct him to
rectify; and the person directly in charge and the other persons
directly responsible, if they are State functionaries, shall be given
administrative sanctions according to law by the units where they
belong or by an organ at a higher level.
Article 58 Where a person, in violation of the provisions of this Law,
commits sexual harassment or domestic violence against a woman, if
such act constitutes a violation of the regulations for administration
of public security, the victim may apply to a public security organ
for an administrative sanction against the violator according to law,
and may also bring a civil suit in a people’s court according to law.
Article 59 Where an entity, in violation of the provisions of this
Law, decries and damages a woman’s personality through the mass media
or by other means, the department of culture, radio, film and
television, the press and publication, or a relevant department shall,
in compliance with their respective functions and powers, instruct it
to rectify and give it an administrative sanction according to law.
Chapter IX Supplementary Provisions
Article 60 The standing committees of the people's congresses of
provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the
Central Government may formulate measures for implementation on the
basis of this Law.
The people's congresses of national autonomous areas may formulate
regulations with appropriate adaptations or supplements in accordance
with the principles laid down in this Law and in light of the specific
conditions of the local ethnic women. The regulations formulated by
autonomous regions shall be submitted to the Standing Committee of the
National People's Congress for approval before going into effect; the
regulations formulated by autonomous prefectures or autonomous
counties shall be submitted to the standing committees of the people's
congresses of the relevant provinces, autonomous regions, or the
municipalities directly under the Central Government for approval
before going into effect, and shall be submitted to the Standing
Committee of the National People's Congress for the record.
Article 61 This Law shall go into effect as of October 1, 1992.
Printer-Friendly E-Mail This
back
http://www.npc.gov.cn/englishnpc/Law/2007-12/13/content_1384122.htm
accessed 24 March 2011
 SECRETARÍA DE INSPECCIONES REGISTROS URBANOS Y TRÁNSITO SUBSECRETARÍA DE
SECRETARÍA DE INSPECCIONES REGISTROS URBANOS Y TRÁNSITO SUBSECRETARÍA DE ANEXĂ LA CONVENŢIACADRU PRIVIND EFECTUAREA STAGIULUI DE PRACTICĂ ÎN
ANEXĂ LA CONVENŢIACADRU PRIVIND EFECTUAREA STAGIULUI DE PRACTICĂ ÎN OFICIAL 3615 ENCUENTRO INTERNACIONAL DE FORMACIÓN PROFESIONAL FABRICACION AVANZADA
OFICIAL 3615 ENCUENTRO INTERNACIONAL DE FORMACIÓN PROFESIONAL FABRICACION AVANZADA CARTA DE PRESENTACIÓN DE LA OFERTA SEÑORES [NOMBRE DE
CARTA DE PRESENTACIÓN DE LA OFERTA SEÑORES [NOMBRE DE DIALECTO CANARIO EL HABLA CANARIA ES UN DIALECTO
DIALECTO CANARIO EL HABLA CANARIA ES UN DIALECTO CARREFOUR PROMOCIONA LOS “PRODUCTOS VALENCIANOS” HASTA EL 27
CARREFOUR PROMOCIONA LOS “PRODUCTOS VALENCIANOS” HASTA EL 27 JOB DESCRIPTION AND PERSON SPECIFICATION (HR5) VACANCY NUMBER 142212GX
JOB DESCRIPTION AND PERSON SPECIFICATION (HR5) VACANCY NUMBER 142212GX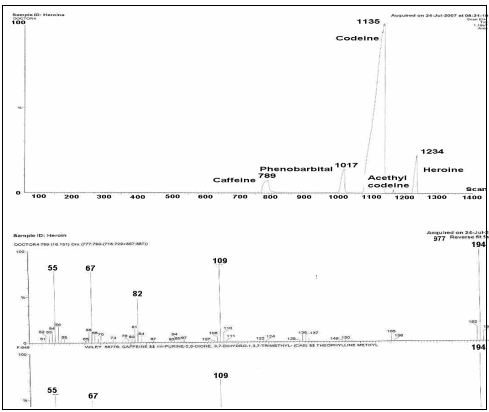 581 FARMACIA 2008 VOLLVI 5 COMPONENT ANALYSIS OF ILLICIT
581 FARMACIA 2008 VOLLVI 5 COMPONENT ANALYSIS OF ILLICIT 2 XXIX CONGRESO ARGENTINO DE PROFESORES UNIVERSITARIOS
2 XXIX CONGRESO ARGENTINO DE PROFESORES UNIVERSITARIOS SERVICIO DE CONTRATACIÓN DE SERVICIOS Y SUMINISTROS DOÑA ANA
SERVICIO DE CONTRATACIÓN DE SERVICIOS Y SUMINISTROS DOÑA ANA