green belt written test study guide code of moral conduct and ethics of cuong nhu oriental martial arts 1 cuong nhu students sho
Green Belt Written Test
Study Guide
Code of Moral Conduct and Ethics of Cuong Nhu Oriental Martial Arts
1
Cuong Nhu students should strive to improve themselves and their
abilities in the martial arts in order to serve the people.
2
All students should be faithful to the ideals of Cuong Nhu
and attempt to spread and develop these beliefs within the younger
generation so that they too will morally and physically fit.
3
All members of Cuong Nhu are unified in spirit
and respect each other and their instructors.
4
Only by absolute discipline of mind, body and spirit
do students maintain honor in Cuong Nhu.
5
All members should respect all other styles of the martial arts and
only use martial arts techniques for self-defense and to protect truth
and reason.
6
Cuong Nhu students through dedicated daily practice
increase their spirit, stamina and moral character.
7
The goal of Cuong Nhu students is to maintain
a pure, simple, sincere and noble life.
8
Self-confidence, self-control, modesty and a non-defeatist
attitude are the mental keynotes for students of Cuong Nhu.
Philosophy Review
ONE GREEN STRIPE
5 Firsts for Friendship
Communicate
Smile
Care
Share
Forgive
5 Steps to Health
Think
Eat
Exercise
Rest
Perform
5 S’s for Warmups
Safety
Slowness
Self awareness
Stretching
Strengthening
5 A’s for Self-Defense
Awareness
Alertness
Avoidance
Anticipation
Action
5 W’s for Self Defense
Wrong time
Wrong place
Wrong people
Wrong attitude
Wrong techniques
5 R’s for Self Defense
Right perspective
Right time
Right place
Right techniques
Run
TWO GREEN STRIPES
5 P’s of Achievers
Perspective
Patience
Perseverance
Pride in accomplishment
Practice ‘til perfect
5 D’s of a Winner
Direction
Discipline
Determination
Dedication
Do ‘til death
5 Think Rights
(No Brain, No Gain)
Think simpler
Think faster
Think better
Think deeper
Think wiser
5 Res’s for Interrelating
Responsibility (self-respect)
Respect Others
Responsiveness
Resolution
Resilience
5 F’s for Learning and Teaching
Fun
Friendship
Focus
Fly your spirit
Finish your goal
5 Re’s of Meditation
Relaxation
Respiration
Renewal/rejuvenation
Reflection
Realization
GREEN BELT
5 Sources of Power
Mind
Body
Spirit
Soul
Ki
7 Main Martial Arts of Influence
Shotokan
Boxing
Judo
Aikido
Wing Chun
Tai Chi Chuan
Vovinam
5 Controls for Self Defense
Control the area (awareness)
Control yourself (fear, anger)
Control the attackers (strategy)
Control the situation
Control the consequences
5 Alls for Self Defense (3-D)
All angles
All levels
All techniques
All situtations
All people
5 Win’s of a Winner
Over yourself
Opponent’s respect
Third party’s respect
Over the situation
People’s hearts
10 Don’ts for Sparring
Angry
Tense
Fearful
Hurried
Waste energy
Overconfident
Distracted
Pre-conceived ideas
Discouraged if you lose
Afraid of losing
Cuong Nhu History
Master Ngo Dong founded Cuong Nhu Oriental Martial Arts in 1965. Cuong
Nhu (pronounced "kung new") combined the hard-style blocks, punches
and kicks of traditional Japanese karate with the shorter, more
circular movements of arts like Aaikido, Wing Chun, Kung Fu and
Vovinam (a Vietnamese art).
To build a strong moral and spiritual foundation for his style, Master
Dong interjected his personal philosophy of self-improvement,
community service, and love and respect for others. In Vietnam, Cuong
Nhu was more than just another form of martial art. It provided an
ideological touchstone for its students, young people who had grown up
in a sadly disjointed, war-torn society that was hard-pressed to meet
their spiritual needs. Master Dong taught martial art techniques to
help his students build themselves up physically, improve themselves,
and personally pursue goals and serve society.
As a child, Master Dong learned Vovinam from his brother, Ngo Quoc
Phong, one of the top five students of Vovinam’s founder, Grand Master
Nguyen Loc. Dong also learned Wing Chun from his two oldest brothers,
who studied with Chinese Master Te Kong. Although their father, Ngo
Khanh Thuc, was then attorney general of northern Vietnam, the Ngo
brothers tested their fighting skills on the street by engaging
hustlers and professional street fighters inhabiting the alleys and
back streets of Hanoi.
After moving south to Hue, Vietnam in 1956, Master Dong began Shotokan
karate training under a former Japanese captain, Choji Suzuki. After
years of fanatical training, Master Dong earned his fourth degree
black belt. He also studied Judo and earned a black belt in that
system. Later, Master Dong studied with American Marine Lt. Ernie
Cates, a Judo and Goshin Jujitsu instructor who had been in the first
U.S. Olympic Judo trials.
Through Master Cates' instruction, Master Dong began to better
understand the spiritual side to the martial arts. He shared training
techniques with Master Cates and eventually combined his broad martial
arts knowledge into his own style, Cuong Nhu, which means "hard-soft"
in Vietnamese. Master Dong has since devoted his life to the
development of Cuong Nhu and to the personal growth of thousands of
students.
In the tradition of early martial arts masters, Master Dong is a civic
leader, as well as a scientist and author. He earned two degrees, in
biology and chemistry, in Vietnam and served as professor of biology
at the University of Hue from 1961 to 1971. After the devastating 1968
Tet offensive, Master Dong organized a civil defense organization, the
People's Self-Defense Forces of Hue, to help protect the public from
the random violence spawned by the war. His organization engaged some
25,000 people in a program of karate, games and friendly competition
to rebuild morale and spirit.
In 1971, he traveled to the United States to pursue a Ph.D. in
entomology at the University of Florida. In September 1971, during his
post-graduate studies, Master Dong opened the first Cuong Nhu Karate
club in the United States. Within two years it grew into the largest
intramural organization on campus. In the spring of 1973, the Cuong
Nhu Karate Association, with a permanent board of directors, was
incorporated to ensure continuity and uniformly high standards of
instruction.
Master Dong earned his doctorate in three years and returned to
Vietnam in 1974. He was then appointed president of Da Nang College.
An outspoken opponent of communism, Master Dong was placed under house
arrest by the communist government of Vietnam in 1975. He and his
family later took the tremendous risk of escaping by boat to
Indonesia. They finally arrived in the United States in November 1977,
on homecoming day at the University of Florida.
Master Dong is president of the Cuong Nhu Oriental Martial Arts
Association, an international organization that oversees the
development of Cuong Nhu. In Vietnam he has published books on
subjects ranging from martial arts philosophy and technique to flower
arrangement. This is the fourth English-language publication of his
Cuong Nhu training manual.
Master Dong is also an accomplished runner. He discovered the joys of
running in 1986 and soon completed his first two marathons, which he
ran on consecutive weekends. His first ultra-marathon was the 100-mile
Western States run in Squaw Valley, Calif. To
date, he has completed 23 marathons, eight 50-mile ultra-marathons and
fourteen 100-mile ultra-marathons.
During a special ceremony at the May 1994 Training Camp, Master Dong
was promoted to 6th degree in Judo. Sensei Ed Szrejter, Executive
Director of the U.S. Judo Association made the presentation. Master
Dong is the 47th Judoka among the USJA's 20,000 members to reach 6th
dan. We were also privileged to share in the promotion of Sensei Ernie
Cates to 7th degree.
Master Dong retired from the University of Florida on August 18, 1994.
He was awarded with dual proclamations from the City of Gainesville
and Alachua County, Florida, declaring August 14, 1994 as Dr. Ngo Dong
Day.
Martial Arts History
Martial arts history in the Orient contains many examples of parallel
as well as synergistic development, both in technique and philosophy.
The indigenous people of each region developed their own methods of
offense and defense. Then, through the mixing pot of centuries of
conflict, these methods evolved from the efforts and insights of both
men and women. As technological innovations replaced skilled warriors
on the battlefield, these martial methods evolved into martial "Ways"
used to train the body and spirit. The major component styles from
which Cuong Nhu is derived all share this evolutionary path.
Vietnamese martial arts began their evolution during the wars against
invaders from surrounding countries and, due to the small stature of
the Vietnamese people, took the soft style approach to self-defense.
In 1253, the first National Martial Arts School was opened at the
Imperial Court, offering degrees (up to Ph.D) in the martial arts.
This school taught empty hand combat, uses of 18 different kinds of
weapons, martial arts tactics, weather forecasting techniques and war
strategies. Some years later, the first martial arts tournament was
held and Tran Quoc Toan became national champion. Fifteenth place went
to a princess named Thuy Tien. Tran Quoc Toan was also nationally
known as a youth hero for helping defeat invading Mongolian troops. At
the age of 16 he had already taken command of an army of teenage
volunteer soldiers.
The people of Binh Dinh province, located in central Vietnam, are
famous for their expertise in the Vietnamese martial arts. Two martial
arts experts from Binh Dinh were Quang Trung, one of Vietnam's kings,
and his female general Bui Thi Xuan. Xuan was the chief instructor of
a martial arts school and proved her expertise by defeating a tiger to
save the life of a man she later married. She was renowned for her
courage and leadership.
In 1946, Grand Master Nguyen Loc systematized the different styles of
the Vietnamese martial arts and named the resulting art vovinam (vo:
martial arts, vinam: abbreviation for Vietnam). His successor, Le Van
Sang, later changed the name to viet vo dao (viet: Vietnam, vo:
martial arts, dao: the Way).
The basis for Shaolin boxing or kung fu was introduced in 540 A.D.,
when an Indian Monk named Bodhidharma, the leader of Zen Buddhism,
traveled to northern China to lecture on Buddhism. He taught in the
Shaolin temple, where the monks were in such poor physical condition,
he supplemented their long hours of motionless meditation with a
series of 18 exercises to improve breathing, circulation and
coordination of body and mind. He created an external form emphasizing
the limbering of joints, bones and muscles, mobility and unity of hard
and soft. This method of training was enriched by the traditional
Chinese martial arts.
Frequent temple burnings during this period of history drove the monks
from the temple. Their arts spread throughout Asia. From this period
came the saying, "Northerners are kickers and Southerners are
punchers." Those monks driven to the north became horsemen and
mountain climbers and therefore developed strong legs and techniques
to capitalize on them. Those in the southern region excelled in hand
techniques since they used their hands for boating and fanning.
In the 14th century during the Yuan dynasty, Master Chang San-feng, a
Taoist priest, studied tao yin, an early Chinese breathing art, that
was the forerunner of tai chi. Considered the founder of Yang style
tai chi chuan (the ultimate fist), he introduced and systematized this
internal form of martial art. It focused on the training of bones and
muscles, overcoming an opponent at the moment of attack and
controlling breathing and movement from the slowest to the fastest.
Yim Wing Chun, whose name means "forever springtime," was a woman who
studied kung fu under the Buddhist nun, Ng Mui. The style she taught
dealt with close combat and economy of movement. Yim, it is told,
witnessed a fight between a crane and a snake and incorporated the
skills of both animals and the training she received from Mui to
develop Wing Chun.
The development of Okinawan martial arts was strongly influenced by
Chinese fighting techniques. Shaolin kung fu eventually reached
Okinawa and developed into the local art known as Okinawa-te. Chinese
missionaries and merchants brought more martial arts techniques to
Okinawa, and many Okinawan masters traveled to China to further their
training. By the 17th century, Okinawa was under Japanese domination,
and national policy forbade the possession of weapons. In this hostile
environment, Okinawa-te evolved into karate (kara: Chinese, te: hand)
and became tremendously important as a means of self-defense.
In 1922, Master Gichin Funakoshi, then president of the Okinawan
Martial Arts Promotion Society, gave impressive demonstrations in
Japan. He attracted a large number of students and remained there to
teach karate. Many Okinawan masters followed Master Funakoshi and
established their schools throughout Japan. Funakoshi, like many
martial arts masters, was multitalented. The name of his style,
shotokan (sho; writing, do: the Way, kan: house or hall), came from
Funakoshi's pen name, "Shoto," and was a tribute to his mastery of
calligraphy. It was Funakoshi, in fact, who changed the writing of the
term karate to mean the art of the empty hand (kara: empty, te: hand).
Grappling, wrestling and throwing techniques were parts of traditional
Japanese combat training and have survived in many forms into modern
times. All are generally characterized by simple, decisive movements.
For example, jujitsu (ju: soft, yielding, jitsu: techniques),
formalized by Hisamori Takenouchi in 1532, advocates close combat
techniques of striking to vital target areas, throwing, joint locking
and choking.
In 1882, Master Jigoro Kano, an expert in jujitsu, created a new
martial art by eliminating jujitsu's lethal elements and adding rules
and regulations. He called his new art kodokan judo. Judo (ju: soft,
do: the Way) means gentle Way. It involves anticipating an opponent's
attack, unbalancing and throwing the opponent using minimum effort, or
using locks and immobilizations. A judoka trains in free form attack,
free falling and discovering the opponent's weaknesses and responding
to his movements.
Also evolving from jujitsu was aikido (ai: combine, ki: internal
strength, do: the Way), a defensive art involving joint manipulations,
throws and some elements of kendo. It advocates the coordination of
mind and body, harmonizing the use of the attacker's weight and
strength to the defender's advantage. In 1938, the first aikido school
was established under Master Morihei Ueshiba, the founder. A soft
style martial art, aikido is a very spiritual practice, the essence of
which is love.
Start The Revolution Within Yourself
O Sensei Ngo Dong, Founder
 PIELIKUMS NR2 IEPIRKUMA IDENTIFIKĀCIJAS NR APES ND 20154 PRETENDENTA
PIELIKUMS NR2 IEPIRKUMA IDENTIFIKĀCIJAS NR APES ND 20154 PRETENDENTA A NTHRAX ICT NEGATIVE CASE REPORT 1 DATA THIS
A NTHRAX ICT NEGATIVE CASE REPORT 1 DATA THIS “ LA QUALITÀ DELLE PROFESSIONI INFORMATICHE NELLA PA UNA
“ LA QUALITÀ DELLE PROFESSIONI INFORMATICHE NELLA PA UNA AANMELDINGSFORMULIER VO 20202021 (IN TE VULLEN DOOR DE BASISSCHOOL)
AANMELDINGSFORMULIER VO 20202021 (IN TE VULLEN DOOR DE BASISSCHOOL) NOBO2554V3 HAL 22 BAUK DIR BORANG UBMNRT KELUAR MASUK
NOBO2554V3 HAL 22 BAUK DIR BORANG UBMNRT KELUAR MASUK GRAN SUIZA ALPINA REF B 1516 6 DÍAS DESDE
GRAN SUIZA ALPINA REF B 1516 6 DÍAS DESDE OPRACOWAŁA MGR JADWIGA ŁAPIŃSKA SPRAWDZIAN Z MATEMATYKI DLA
OPRACOWAŁA MGR JADWIGA ŁAPIŃSKA SPRAWDZIAN Z MATEMATYKI DLA •RI ISBN 9739296335 BUCUREŞTI 2002 ARHETIP EMAIL
•RI ISBN 9739296335 BUCUREŞTI 2002 ARHETIP EMAIL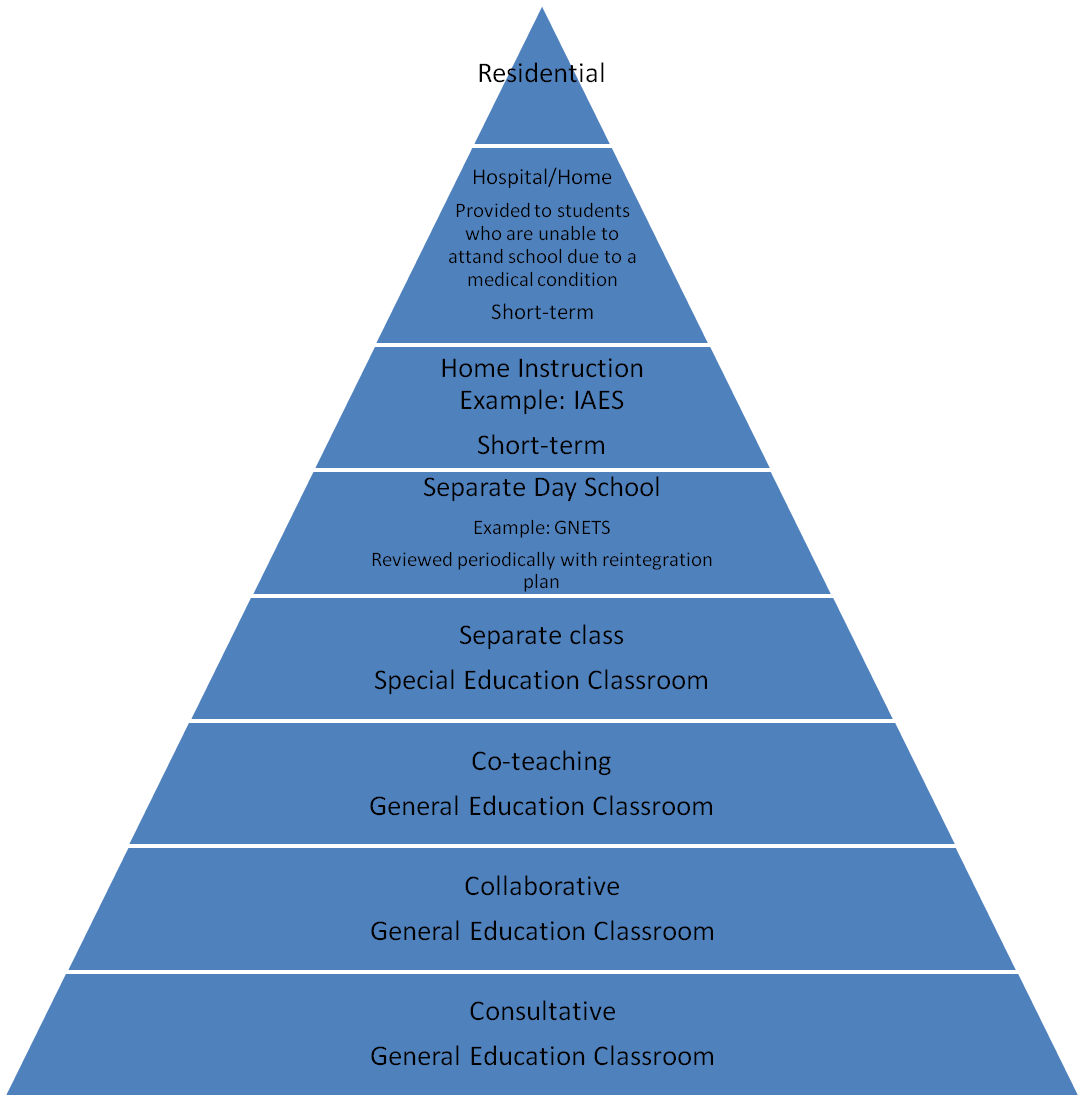 LEAST RESTRICTIVE ENVIRONMENT ALL STUDENTS WHO RECEIVE SPECIAL EDUCATION
LEAST RESTRICTIVE ENVIRONMENT ALL STUDENTS WHO RECEIVE SPECIAL EDUCATION